In the event of a cardiac arrest, follow these CPR guidelines. For more free resources like our ACLS cardiac arrest algorithm, explore other online articles to sharpen your life-saving skills.
Note: These guidelines are for an adult cardiac arrest algorithm. Review guidelines for the pediatric cardiac arrest algorithm with our free resources.
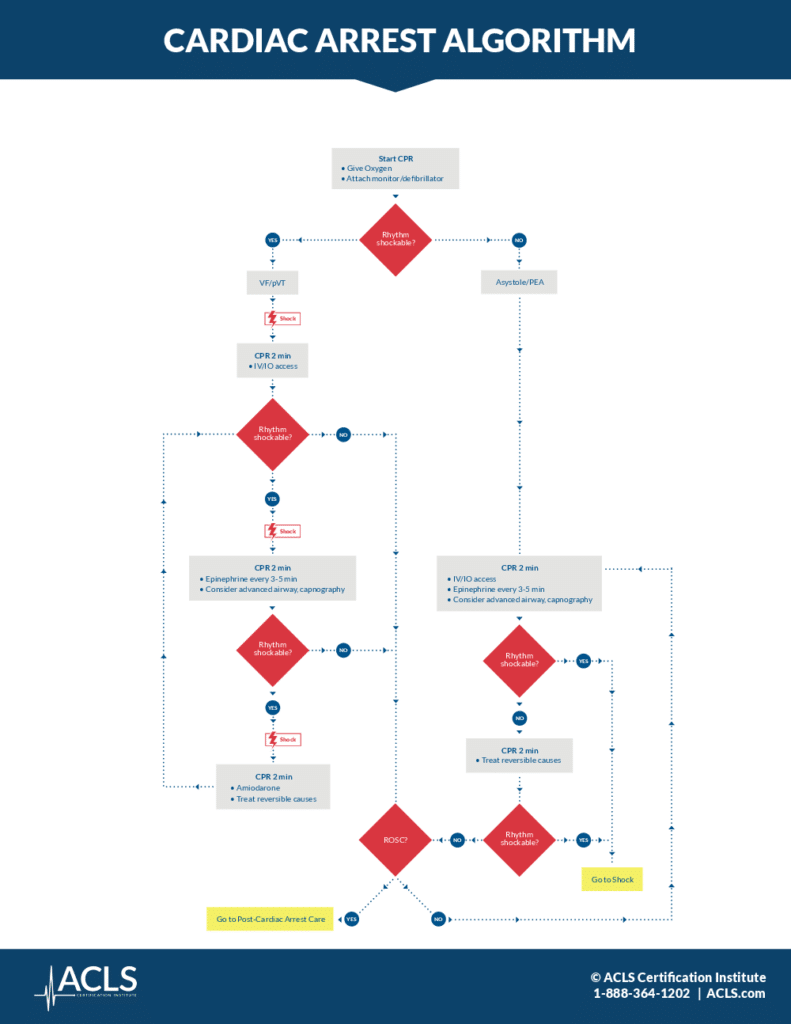
- Start CPR. Start CPR with hard and fast compressions, around 100 to 120 per minute, allowing the chest to completely recoil. Give the patient oxygen and attach a monitor or defibrillator. Make sure to minimize interruptions in chest compressions and avoid excessive ventilation, using a 30 to 2 compression-to-ventilation ratio if no airway is established.
- Rhythm shockable? Conduct a rhythm check, making sure the pause in chest compressions is not more than 10 seconds.
- VF/pVT (Shockable rhythm). If a shockable rhythm is present, either v-fib or pulseless v-tach, begin the charging sequence on the defibrillator and resume chest compressions until the defibrillator is charged.
- Shock. When the defibrillator is charged, announce the shock warning and make sure no one is touching the patient. Shock the patient with an initial dose of 120 to 200 joules.
- CPR – 2 min. Immediately resume CPR for 2 minutes, and establish IV access.
- Rhythm Shockable? Check for pulse and rhythm for no more than 10 seconds every 2 minutes.
- No. If the patient shows signs of return of spontaneous circulation, or ROSC, administer post-cardiac care. If a nonshockable rhythm is present and there is no pulse, continue with CPR and move to the algorithm for asystole or PEA.
- Yes – Shock. If the rhythm is shockable, announce the shock warning and make sure no one is touching the patient. Administer the shock.
- CPR – 2 min. Continue with CPR for 2 minutes. Give the patient a vasopressor such as epinephrine every 3 to 5 minutes, and consider advanced airway and capnography, giving 1 breath every 6 seconds once the advanced airway is in place.
- Rhythm Shockable? Check for pulse and rhythm for no more than 10 seconds every 2 minutes.
- No. If the patient shows signs of return of spontaneous circulation, or ROSC, administer post-cardiac care. If a nonshockable rhythm is present and there is no pulse, continue with CPR and move to the algorithm for asystole or PEA.
- Yes – Shock. If the rhythm is shockable, announce the shock warning and make sure no one is touching the patient. Administer the shock.
- CPR – 2 min. Continue with CPR for 2 minutes. Consider giving the patient an antiarrhythmic drug such as amiodarone for refractory v-fib or pulseless v-tach, and treat reversible causes. Use Hs and Ts to remember: hypovolemic, hypoxia, hydrogen ions, hypo and hyperkalemia, hypothermia, tension pneumo, tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis.
- Asystole/PEA. If a nonshockable rhythm is present, and the rhythm is organized, check for a pulse. Make sure the pause in chest compressions to check the rhythm is not more than 10 seconds.
- CPR – 2 min. Continue with CPR for 2 minutes, and establish IV access. Give the patient a vasopressor such as epinephrine every 3 to 5 minutes, and consider advanced airway and capnography, giving 1 breath every 6 seconds once the advanced airway is in place.
- Rhythm Shockable? Check for pulse and rhythm for no more than 10 seconds every 2 minutes.
- Yes. If the rhythm changes to a V-fib or V-tach shockable rhythm, move to that algorithm and prepare to shock the patient.
- CPR – 2 min. If a nonshockable rhythm is still present with no pulse, continue with CPR for 2 minutes, and treat reversible causes. Use Hs and Ts to remember: hypovolemic, hypoxia, hydrogen ions, hypo and hyperkalemia, hypothermia, tension pneumo, tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis.
- Rhythm Shockable? Check for pulse and rhythm for no more than 10 seconds every 2 minutes.
- Yes. If the rhythm changes to a V-fib or V-tach shockable rhythm, move to that algorithm and prepare to shock the patient.
- CPR – 2 min. If the patient shows signs of return of spontaneous circulation, or ROSC, administer post-cardiac care. If a nonshockable rhythm is present and there is no pulse, continue with CPR.
Recommended Articles

AEDs for Adults and Children Over 8 Video
In this video, we review the correct operation of the automatic external defibrillator for adults and for children over 8 years old.